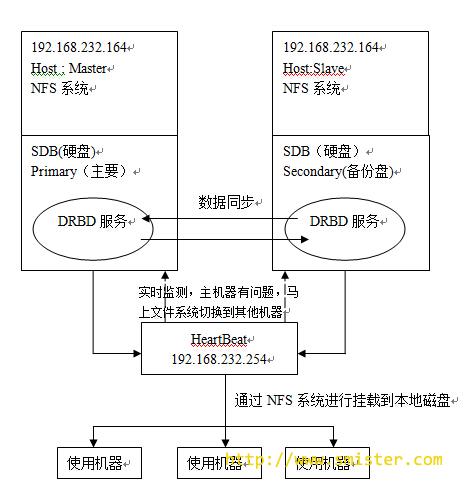
heartbeat的作用就可以增加drbd的可用性,它能在某节点故障后,自动切换drbd块到备份节点,并自动进行虚IP从新绑定,DRBD块提权,磁盘挂载以及启动NFS等脚本操作,这一系列操作因为只在他后端节点间完成,前端用户访问的是heartbeat的虚IP,所以对用户来说无任何感知。
一、配置DBRS ,请查看DBRS配置篇 ,就在下面
二、Heartbeat配置
1、 安装heartbeat(CentOS6.3中默认不带有Heartbeat包,因此需要从第三方下载
(Master , Slave 同样操作)
[root@localhost ~]#wget ftp://mirror.switch.ch/pool/4/mirror/scientificlinux/6rolling/i386/os/Packages/epel-release-6-5.noarch.rpm
//如果版本找不到 , 可以到ftp://mirror.switch.ch/pool/选择新的版本
[root@localhost ~]#rpm –ivUh epel-release-6-5.noarch.rpm
[root@localhost ~]#yum –enablerepo=epel install heartbeat –y
2、 配置beartbeat
(Master)
1) 配置ha.cf配置文件
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/ha.d/ha.cf
#日志
logfile /var/log/ha-log
logfacility local0
#心跳检测时间
keepalive 2
#死亡四件
deadtime 6
#制定对方IP , 这里的网卡需要对应
ucast eth0 192.168.232.165
#服务器正常后由主服务器接口资源 , 另一台放弃资源
auto_failback off
#自定义节点
node Master Slave
2)认证文件authkeys用于配置心跳的加密方式,该文件主要是用于集群中两个节点的认证,采用的算法和密钥在集群中节点上必须相同,目前提供了3种算法:md5,sha1和crc。其中crc不能够提供认证,它只能够用于校验数据包是否损坏,而sha1,md5需要一个密钥来进行认证。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ha.d/ha.cf
[root@localhost ~]# dd if=/dev/random bs=512 count=1 | openssl md5
0+1 records in
0+1 records out
20 bytes (20 B) copied, 0.000126508 s, 158 kB/s
(stdin)= 12f3afe7de1c1a9948444feeacf11479 //获得的md5加密的随机码
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/had.d/authkeys
auth 3
3 md5 12f3afe7de1c1a9948444feeacf11479
//authkeys文件需要更改权限为600 , 否则heartbeat启动会失败
[root@localhost ~]#chmod 600 /etc/had.d/authkeys
3)生成集群资源文件haresource
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ha.d/haresources
Master IPaddr::192.168.232.254/24/eth0 drbddisk::r0 Filesystem::/dev/drbd0::/data::ext3 killnfsd
注:
该文件内IPaddr,Filesystem等脚本存放路径在/etc/ha.d/resource.d/下,也可在该目录下存放服务启动脚本(例如:mysql,www),将相同脚本名称添加到/etc/ha.d/haresources内容中,从而跟随heartbeat启动而启动该脚本。
IPaddr::192.168.7.90/24/eth0:用IPaddr脚本配置浮动VIP
drbddisk::r0:用drbddisk脚本实现DRBD主从节点资源组的挂载和卸载
Filesystem::/dev/drbd0::/data::ext3:用Filesystem脚本实现磁盘挂载和卸载
生成killnfsd文件 , 如果不存在nfs系统请运行yum install nfs -y
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/ha.d/resource.d/killnfsd
killall -9 nfsd ; /etc/init.d/nfs restart;exit 0;
[root@localhost ~]#chmod 755 /etc/ha.d/resource.d/killnfsd
4)生成drbddisk启动脚本
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ha.d/resource.d/drbddisk
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ha.d/ha.cf
[root@localhost ~]# dd if=/dev/random bs=512 count=1 | openssl md5
0+1 records in
0+1 records out
20 bytes (20 B) copied, 0.000126508 s, 158 kB/s
(stdin)= 12f3afe7de1c1a9948444feeacf11479 //获得的md5加密的随机码
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/had.d/authkeys
auth 3
3 md5 12f3afe7de1c1a9948444feeacf11479
//authkeys文件需要更改权限为600 , 否则heartbeat启动会失败
[root@localhost ~]#chmod 600 /etc/had.d/authkeys
#!/bin/bash
#
# This script is inteded to be used as resource script by heartbeat
#
# Copright 2003-2008 LINBIT Information Technologies
# Philipp Reisner, Lars Ellenberg
#
###
DEFAULTFILE="/etc/default/drbd"
DRBDADM="/sbin/drbdadm"
if [ -f $DEFAULTFILE ]; then
. $DEFAULTFILE
fi
if [ "$#" -eq 2 ]; then
RES="$1"
CMD="$2"
else
RES="all"
CMD="$1"
fi
## EXIT CODES
# since this is a "legacy heartbeat R1 resource agent" script,
# exit codes actually do not matter that much as long as we conform to
# http://wiki.linux-ha.org/HeartbeatResourceAgent
# but it does not hurt to conform to lsb init-script exit codes,
# where we can.
# http://refspecs.linux-foundation.org/LSB_3.1.0/
#LSB-Core-generic/LSB-Core-generic/iniscrptact.html
####
drbd_set_role_from_proc_drbd()
{
local out
if ! test -e /proc/drbd; then
ROLE="Unconfigured"
return
fi
dev=$( $DRBDADM sh-dev $RES )
minor=${dev#/dev/drbd}
if [[ $minor = *[!0-9]* ]] ; then
# sh-minor is only supported since drbd 8.3.1
minor=$( $DRBDADM sh-minor $RES )
fi
if [[ -z $minor ]] || [[ $minor = *[!0-9]* ]] ; then
ROLE=Unknown
return
fi
if out=$(sed -ne "/^ *$minor: cs:/ { s/:/ /g; p; q; }" /proc/drbd); then
set -- $out
ROLE=${5%/**} : ${ROLE:=Unconfigured} # if it does not show up
else
ROLE=Unknown
fi
}
case "$CMD" in
start)
# try several times, in case heartbeat deadtime
# was smaller than drbd ping time
try=6
while true; do
$DRBDADM primary $RES && break
let "--try" || exit 1 # LSB generic error
sleep 1
done
;;
stop)
# heartbeat (haresources mode) will retry failed stop
# for a number of times in addition to this internal retry.
try=3
while true; do
$DRBDADM secondary $RES && break
# We used to lie here, and pretend success for anything != 11,
# to avoid the reboot on failed stop recovery for "simple
# config errors" and such. But that is incorrect.
# Don't lie to your cluster manager.
# And don't do config errors...
let --try || exit 1 # LSB generic error
sleep 1
done
;;
status)
if [ "$RES" = "all" ]; then
echo "A resource name is required for status inquiries."
exit 10
fi
ST=$( $DRBDADM role $RES )
ROLE=${ST%/**}
case $ROLE in
Primary|Secondary|Unconfigured)
# expected
;;
*)
# unexpected. whatever...
# If we are unsure about the state of a resource, we need to
# report it as possibly running, so heartbeat can, after failed
# stop, do a recovery by reboot.
# drbdsetup may fail for obscure reasons, e.g. if /var/lock/ is
# suddenly readonly. So we retry by parsing /proc/drbd.
drbd_set_role_from_proc_drbd
esac
case $ROLE in
Primary)
echo "running (Primary)"
exit 0 # LSB status "service is OK"
;;
Secondary|Unconfigured)
echo "stopped ($ROLE)"
exit 3 # LSB status "service is not running"
;;
*)
# NOTE the "running" in below message.
# this is a "heartbeat" resource script,
# the exit code is _ignored_.
echo "cannot determine status, may be running ($ROLE)"
exit 4 # LSB status "service status is unknown"
;;
esac
;;
*)
echo "Usage: drbddisk [resource] {start|stop|status}"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
[root@localhost ~]# chmod 755 /etc/ha.d/resource/drbddisk
5)将上面新建的文件复制给Slave文件
[root@localhost ~]# scp /etc/ha.d/ha.cf root@192.168.232.165:/etc/ha.d/
[root@localhost ~]# scp /etc/had.d/authkeys root@192.168.232.165:/etc/ha.d/
[root@localhost ~]# scp /etc/ha.d/haresources root@192.168.232.165:/etc/ha.d/
[root@localhost ~]# scp /etc/ha.d/resource.d/drbddisk root@192.168.232.165:/etc/ha.d/resource/
(以下是Slave操作)
6)更改Master传过来的文件 , 到那时只改ha.cf就可以了
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ha.d/ha.cf
//以后一下的内容就好
Ucast eth0 192.168.232.165
三、启动heartbeat并测试
(Master , Slave操作)
1、启动
[root@localhost ~]# service heartbeat start
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig heartbeat on
2、 测试 , ping heartbeat中生成的虚拟ip是否成功
[root@localhost ~]# ping 192.168.232.254
四、配置NFS
(Master , Slave操作)
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/exports/data
*(rw,no_root_squash)
//重启NFS服务
[root@localhost ~]# service rpcbind restart
[root@localhost ~]# service nfs restart
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig rpcbind on
//开机不启动nfs , 因为启动heartbeat的脚本就已经启动nfs了
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig nfs off
五、测试
在另外一台linux客户端中挂载虚ip : 192.168.232.254 , 挂载成功表示整个实验成功了
这里我就在slave测试
1)挂载nfs系统
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /test
[root@localhost ~]# mount –t nfs 192.168.232.254:/data /test
[root@localhost ~]# df –h
[root@localhost ~]# cd /test
[root@localhost ~]# ls
//如果刚刚测试的数据都在 , 证明OK了
[root@localhost ~]#touch ttt
//测试能不能写入
2)测试当primary挂掉时 , 看备份的机子成功接管Primary
(Master操作)
[root@localhost ~]# init 0
(Slave操作)
[root@localhost ~]# service drbd status
//如果出现提升为primary证明系统成功切换
[root@localhost ~]# cd test
//再来回查挂载的系统能不能使用 版权声明:未经博主允许不得转载。http://smister.com/post-25.html